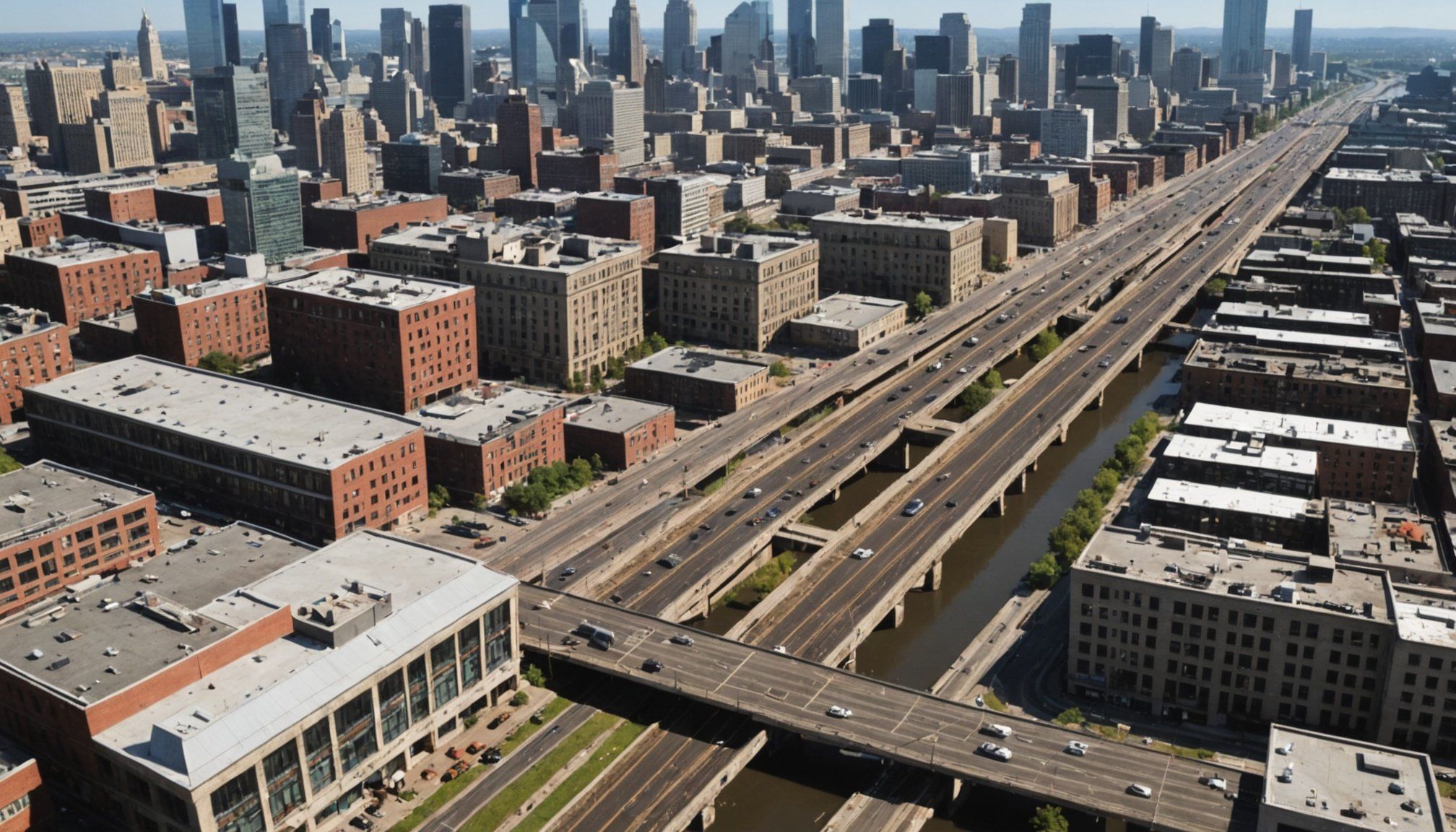
Introduction to Urban Infrastructure Developments
Urban infrastructure is the backbone of cities, facilitating everything from transportation to utilities. It encompasses essential systems and structures, like roads, bridges, water supply networks, and waste management. This infrastructure is vital for supporting the daily functioning and quality of life of urban populations, enabling smooth transit and efficient services.
In recent years, development trends in urban areas have been shifting towards environmentally friendly and technologically advanced solutions. One significant trend is the integration of smart technologies into urban planning, such as intelligent traffic systems and green buildings, which aim to reduce environmental impact while improving efficiency. Another key trend is the prioritization of sustainable public transportation options to reduce reliance on private vehicles, aiming to cut down urban congestion and pollution.
Also read : Unlocking Home Equity: Top Strategies for Using Equity Release to Fund Your Property Renovations
City planning is a collaborative effort involving both government and private sector participation. Governments typically lead the planning processes, setting regulations and overseeing public infrastructure projects. They ensure that infrastructure aligns with broader urban development goals and public interests. Meanwhile, the private sector often partners in the actual construction and maintenance of infrastructure, bringing expertise, innovation, and capital to the table. This teamwork allows for more dynamic and responsive urban development, meeting the growing demands of modern city life.
Relationship Between Urban Infrastructure and Property Insurance
The impact of urban infrastructure on property insurance is considerable, with risk assessment being a pivotal aspect for insurers. As cities evolve, infrastructure enhancements or degradation directly influence risk profiles. Improved infrastructure, like elevated flood defences, tends to reduce risk, potentially lowering property insurance premiums. Conversely, outdated or failing infrastructure can lead to increased risks and higher costs due to higher claims probabilities.
Have you seen this : Navigating the Obstacles: Securing a Mortgage for Multi-Unit Properties
Statistically, there’s a notable correlation between infrastructure developments and insurance costs. For instance, investments in road safety or drainage systems are shown to reduce incident severity, thus impacting how insurance providers assess risk. As infrastructure enhances urban safety, the perceived potential for property damage decreases, influencing lower premiums.
Case studies from major cities shed light on these dynamics. In San Francisco, the introduction of seismic retrofitting laws reduced earthquake risk, positively influencing property insurance premiums. Similarly, in Miami, the implementation of advanced water management systems has led to adjustments in flood insurance rates. These cases exemplify how infrastructure can play a direct role in shaping insurance landscapes.
Understanding these correlations enables both property owners and insurers to make informed decisions and underscores the crucial relationship between urban planning and property insurance.
Regulatory Framework Influencing Insurance Policies
In the complex world of insurance policies, the regulatory environment significantly influences how these policies are shaped, especially when it comes to property insurance. Urban infrastructure is often subject to an intricate web of regulations designed to ensure safety and sustainability. These regulations can have a profound impact on property insurance, dictating how insurers assess risk and determine premiums.
Local policies play a pivotal role in this dynamic. For instance, stringent building codes and safety measures can lead to reduced insurance premiums, as they lower the risk of potential damage. Conversely, regions with lax regulations may see higher insurance policies due to perceived risks. Thus, the interaction between local policies and the insurance market is a delicate balance of compliance and risk assessment.
Experts frequently discuss the need for regulatory changes that might enhance insurance response capabilities. Proposed changes often focus on modernising existing policies to better address contemporary challenges, such as climate change and urban expansion. By adjusting the regulatory environment, these measures aim to create a more resilient insurance market that protects stakeholders’ interests while fostering industry growth. Implementing these changes requires collaboration between government bodies, insurers, and policymakers to ensure that the evolving needs of property owners are adequately met.
Risk Management Strategies for Insurers
Navigating urban planning shifts is an essential facet of modern insurance strategies. Insurers must adapt to evolving cityscapes by employing robust risk management techniques. One common approach is the analysis of data trends alongside emerging technologies to anticipate potential risks associated with urban development. Advanced analytics — leveraging geographic information systems (GIS) and predictive modelling tools — help insurers understand the dynamic nature of cities.
An effective method of risk management involves proactive insurance strategies that anticipate potential threats in densely populated areas. These strategies might include diversifying insurance portfolios geographically or partnering with local governments to stay informed on impending urban planning changes. Importantly, insurers should also consider the unique risk management challenges that come with infrastructure upgrades, such as enhanced flood barriers or newly implemented transportation systems.
Insurers are recommended to engage with stakeholders, including urban developers and policymakers, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of future challenges in urban development. Constructing scenario-based models aids in visualising how various urban strata and infrastructure investments impact risk profiles. By refining these insurance strategies, companies can achieve resilience against unforeseen events, maintaining stability in an ever-changing landscape. This ensures insurers remain both agile and responsive, providing clarity and confidence to their clients.
Case Studies of Infrastructure Impacts on Insurance
In addressing the complexities of insurance outcomes resulting from various urban development projects, this section delves into notable case studies that provide insightful perspectives.
Case Study 1: Coastal City Infrastructure and Flood Insurance
In a significant case, a coastal city invested heavily in advanced flood defences, aiming to mitigate the increasing risk of flooding due to climate change. As a direct outcome, insurance premiums for property owners in the area saw a notable decrease. This reduction highlights the insurance industry’s trust in the city’s enhanced capabilities to manage flood risk. Moreover, the flood defence system’s efficacy improved the overall risk perception among residents and insurers alike. Despite the upfront costs associated with building robust infrastructure, the long-term savings in insurance premiums presented persuasive evidence for such investments.
Case Study 2: Urban Renewal Projects and Property Values
An urban renewal project altering a deteriorating district into a vibrant commercial hub prompted a significant upsurge in local property values. Consequently, insurance companies adjusted their policies to reflect heightened property values and lowered associated crime risks. This case study illustrates the direct correlation between urban development initiatives and insurance outcomes, benefitting both property owners and local economies.
Case Study 3: Transportation Infrastructure Improvements and Risk Perception
Enhancements in a city’s transportation infrastructure, including expanded public transit lines, improved urban mobility while significantly altering perceptions of risk across several neighbourhoods. The transportation improvements and decreased travel times contributed to a more positive view of the area, encouraging lower insurance premiums. Insurers recognised the potential for reduced accident incidents and property risks associated with isolated regions now better connected by state-of-the-art transit systems.
Conclusion and Future Directions
As urban development progresses, it significantly influences the insurance landscape. Predicted future trends in urban infrastructure are poised to reshape property insurance in essential ways. Increasing urbanisation leads to denser constructions, which heightens the complexity of risk assessment and demands evolving strategies in insurance evolution.
Current emerging trends suggest an integration of advanced data analytics and smart technologies. This helps in assessing urban risks more comprehensively, providing insurers with precise tools to evaluate potential claims. This evolution underscores the importance of continuous research and adaptation to meet dynamic urban challenges.
Another critical aspect revolves around the environmental implications of urbanisation. Insurers need to consider the amplified risk of natural disasters and climate-change-related events. Responsible insurance evolution could entail adapting policies to cover new risk parameters specific to urban settings. Furthermore, insurers must acknowledge how urban developments, such as smart cities and green buildings, impact risk profiles differently than traditional constructions.
Ultimately, aligning insurance evolution with urban development trends will ensure comprehensive coverage and support for policyholders in ever-evolving urban environments. By staying abreast with these developments, insurers can offer more sophisticated solutions, thereby reinforcing their role in the future of urban habitation.